Learn about the principle, types, and applications of precipitation titration, which involves the formation of precipitate during the titration technique.
Chemical analysis plays an important role in the study of the composition of substances or materials. It is broadly divided into two types qualitative and quantitative analysis. Titration is also known as titrimetry or volumetric analysis.
It is an analytical technique used to estimate the concentration of an analyte in a sample solution that is widely used in chemistry laboratories since it offers several applications and advantages.
Titration is carried out by using a burette containing a titrant with known concentration is placed above the conical flask or beaker of a solute. The titrant is added until the reaction is complete; the endpoint or equivalence point is usually indicated with an indicator.
There are many different forms of titration such as acid-base titrations, redox titrations (oxidation-reduction), precipitation titrations, and complexometric titrations, in which each type involves a different type of chemical reaction.
What is precipitation titration with example?
Precipitation titration is a type of titration that involves the formation of a precipitate during the titration process. Precipitation titration refers to volumetric methods based on the formation of a slightly soluble precipitate, whereas the precipitating titration based on the use of silver nitrate (AgNO3) as a precipitating agent is known as the argentometric method.
In a precipitate titration, the titrant reacts with the solute to produce an insoluble substance (precipitate). It continues until all of the solutes have been consumed in which uses silver ions to determine chloride levels.
It is an important technique for determining halogens and certain metal ions. Precipitation titration is an important topic for class 12.
Precipitation titration example:
To estimate the chloride ion concentration in a sample solution, we can titrate it with a known concentration of silver nitrate solution.
The following chemical reaction takes place:
Ag+(aq) + Cl–(aq)→ AgCl(s).
- During the titration, AgCl settles to the bottom of the conical flask in the form of a white precipitate.
- The amount of silver ion used to reach the equivalence point is the same as the amount of chloride ion present at the start. The amount of silver ion used for the equivalence point is the same as the amount of chloride ion originally there.
- Use n = cV to calculate the number of moles of silver or chloride ion.
What is the principle of precipitation titration?
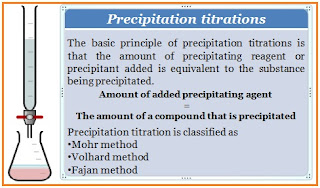
The basic principle of precipitation titrations is that the amount of precipitating reagent or precipitant added is equivalent to the substance being precipitated.
Amount of added precipitating agent = the amount of a compound that is precipitated
Precipitation titration curves:
The change in concentration of either a titrant or a titrand as a function of the titrant's volume is followed by a precipitation titration curve.
- The precipitation titration curves are represented by:
- During titration, the concentration of reactants changes
- When using the indicators, there is a chance of titration error
- The conditions at the equivalent point
Indicators used in precipitation titration:
For precipitation titration, there are three types of indicators are used, two of them are used chloride ions, while one is used cation silver.
- In Mohr's titration, silver nitrate, or potassium chromate can use as an indicator to determine the concentration of chloride, which produces red silver chromate.
- In Volhard’s titration, the ferric ion can use as an indicator to determine the silver ions, which produces red-brown color.
- In Fajan’s titration, the dye dichlorofluorescein can use as an indicator to the determination of chloride, the endpoint being identified by the green suspension turning pink.
Determination of endpoint in precipitation titrations:
Ag+ titrations are known as argentometric titrations. To identification of endpoint in argentometric titration, three traditional methods based on color indicators can be used.
- In Mohr's titration, the formation of colored precipitate at the endpoint
- In Volhard’s titration, the formation of a soluble, colored complex at the endpoint
- In Fajan’s titration, adsorption of a colored indicator on the precipitate at the endpoint
Types of precipitation titration:
There are three types of precipitation titration. According to the type of application and endpoint detection method, precipitation titration is classified as the Mohr method, Volhard method, and Fajan method.
Mohr method:
It is a type of precipitation titration used to determine the chlorides by titration with silver nitrate. It uses chromate ions (CrO42-) as the indicator, for the argentometric determination of bromide, cyanide and, chloride ions.
Volhard method:
The Volhard method is a type of precipitation titration to determine the bromine, chlorine, and iodine in the halide by precipitating it with excess silver nitrate and titrating the excess by addition with standard potassium thiocyanate (KSCN). It is performed in an acidic solution.
Fajan method:
It is a type of precipitation titration in which the reaction between the produced precipitate and the predictor is used in this method. Dichlorofluorescein is used as an indicator that acts as an anion in the solution.
Applications of precipitation titration:
- Precipitation titration is most commonly applied for reactions where the titration cannot be recognized by changing the color.
- The determination of halide ions or silver content using a sodium chloride (NaCl) solution is a typical use of precipitation titration.
- The concentration of ions in the analyte sample can be determined using this method.
- It is used to determine the salt content in water, food, and drinks, etc.
- It has pharmaceutical applications also, such as analysis of carbromal, infusion of sodium chloride (NaCl), and potassium chloride (KCl) infusion, etc.
What is the importance of precipitation titration?
Precipitation titration is an important method in chemistry as it allows for an accurate determination of halogens and some metal ions concentration in the sample solution.
You may also like this
No comments:
Post a Comment