Learn how to make different concentrations of molar and normal hydrochloric acid solutions, which are needed for many applications such as research, practical, pharmaceutical, chemical laboratory, and industries, etc.
The molecular weight of HCl is 36.458 g/mol
The boiling point of HCl is -85.05 °C
The density of HCl is 1.49 kg/m³
The specific gravity of HCL is 1.19 g/ml
Generally, a liquid form of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in different concentrations is supplied in the market by vendors.
Requirements of glassware and apparatus:
Digital balance, beaker, pipette, pipette bulb, volumetric flask, measuring cylinder, glass rod, distilled water, AR/LR grade hydrochloric acid (HCl), etc.
| Table of Contents: |
Normality is a measure of concentration that is equal to the gram equivalent weight of solute per liter of solution. Gram equivalent weight is a measure of the reactive capacity of a molecule. Normality is used to measure the concentration of acid or base in the solution. Unit of normality is Eq/L.
For example,
1M hydrogen chloride provides 1M hydrogen ions and 1M chloride ions into the solution. 1M of hydrogen ions is equal to one equivalent of hydrogen ions. 1M HCl is equivalent to 1N HCl because HCl is a monobasic acid, It has the same molecular mass and equivalent mass.
To make a 0.1 M HCl solution, we usually need to dilute it with water from a stock solution or concentrated HCl. Most concentrated hydrochloric acid is present in 37.5%. There are several methods for calculating; of these, we can use the most precise method, which is the normality calculation for dilution.
Calculation method:
Grams of compound required = (N desired) (equivalent mass) (desired volume in liters)
Volume of concentrated acid required = (grams of acid required)/ (% concentration x specific gravity).
We must first determine the normality before diluting 0.1 M HCl from a 37.5 percent concentrated HCl solution. Simply multiplying 0.1 M by 1 will give 0.1 N.
Equivalent mass is the molar mass divided by the number of hydrogen ions. HCl has a molar mass of 36.4611 g/mol. It’s because it only has one hydrogen ion.
Enter the details in the formula:-
Grams of compound required = (0.1 N) (36.4611)(1 Liter) = 3.6461
Volume of concentrated acid required = (3.6461)/(0.375 x 1.189) = 8.1774 ml
Therefore, 8.1774 ml of 37.5% concentrated hydrochloric acid is required to prepare 0.1 M HCl.
How to prepare 0.01N HCl solution?
Take 0.818 ml of 37.5% hydrochloric acid using a pipette, dilute to 1000 ml of distilled water in a volumetric flask. Allow the solution to cool to ambient temperature and properly mix it.
How to prepare 0.05N HCl solution?
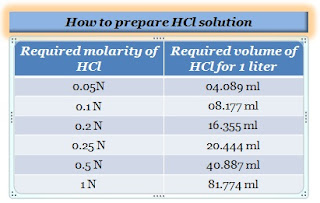
Take 04.089 ml of 37.5% hydrochloric acid using a pipette, dilute to 1000 ml of distilled water in a volumetric flask. Allow the solution to cool to ambient temperature and properly mix it.
How to prepare 0.1N HCl solution?
Take 8.177 ml of 37.5% hydrochloric acid using a pipette, dilute to 1000 ml of distilled water in a volumetric flask. Allow the solution to cool to ambient temperature and properly mix it.
How to prepare 0.2N HCl solution?
Take 16.355 ml of 37.5% hydrochloric acid using a pipette, dilute to 1000 ml of distilled water in a volumetric flask. Allow the solution to cool to ambient temperature and properly mix it.
How to prepare 0.25N HCl solution?
Take 20.444 ml of 37.5% hydrochloric acid using a pipette, and slowly dilute to 01 liters distilled water in a volumetric flask. Allow the solution to cool to ambient temperature and properly mix it.
How to prepare 0.5N HCl solution?
Take 40.887 ml of 37.5% HCL using a pipette, and slowly dilute to 01-liter distilled water in a volumetric flask. Allow the solution to cool to ambient temperature and properly mix it.
How to prepare 1N HCl solution?
Take 81.774 ml of 37.5% HCL, and slowly dilute to 1000 ml of distilled water in a volumetric flask. Allow the solution to cool to ambient temperature and properly mix it.
2N hydrochloric acid solution preparation:
Take 16.35 ml of 37.5% HCL using a pipette, and carefully dilute to 100 ml of distilled water in a volumetric flask. Allow the solution to cool to ambient temperature and properly mix it.
5N hydrochloric acid solution preparation:
Take 40.88 ml of 37.5% HCL, carefully dilute to 100 ml of distilled water in a volumetric flask. Allow the solution to cool to ambient temperature and properly mix it.
6N hydrochloric acid solution preparation:
Take 122.66 ml of 37.5% HCL, carefully dilute to 250 ml of distilled water in a volumetric flask. Allow the solution to cool to ambient temperature and properly mix it.
How to prepare 0.1 N HCl from 1 N HCl?
Using a pipette, dilute 10.00 ml of prepared 1N HCl solution to 100 ml of water in a volumetric flask, the resulting solution is 0.1N hydrochloric acid.
How to prepare 1 m HCl from 37.5% HCl?
Using a pipette, dilute 08.18 ml of 37.5% HCl to 100 ml of water in a volumetric flask, the resulting solution is 0.1M hydrochloric acid.
How to prepare 10 HCl from 36.5 % HCl solution?
We can calculate it by using the following formula i.e. C1V1=C2V2,
V1= 10*100/36.5=27.39 ml
Using a pipette, carefully dilute 27.39 ml of 36.5% HCl to 100 ml of water in a volumetric flask, the resulting solution is 10% hydrochloric acid.
Note:
- Hydrochloric acid is an extremely dangerous acid upon contact. Therefore follow laboratory safety measures (SOP) and please use extreme caution when preparing the solution concentrations.
- When making acid solutions, it is recommended that always add (gradually) acid to water.
- Stir a little amount of HCl into a large volume of water at a time, and then dilute the solution.
- When handling HCl, always wear a chemical-resistant apron, gloves, and goggles to protect your eyes and skin.
- Since concentrated hydrochloric acid is toxic when inhaled, it should always be handled in a fume hood.
- Acid should be kept in a special cabinet made of wood. Since metal corrode rapidly when exposed to hydrochloric acid vapors, wooden cabinets are better than metal cabinets for acid storage.
- If acid splashes on your skin or in your eyes, wash it off with water for 15 to 20 minutes.
References:
- Indian Pharmacopoeia 1996
- Wikipedia contributors, 'Hydrochloric acid', Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, 13 January 2022, 18:16 UTC, Available Here
- ‘Use of Sulfuric Acid & Phosphoric Acid in Titration’. Sciencing, Available Here
- What Is the Difference between Molarity and Normality? Westlab. Available Here
- Acid & Base Normality and Molarity Calculator. Available Here
No comments:
Post a Comment