Dosage forms have different types that depend on the route of drug delivery/method and can also be classified based on their physical form.
Dosage forms are pharmaceutical products that are particular mixtures of drug and excipients and are prepared in various ways in a special configuration such as solid-liquid, semi-solid, and gaseous dosage forms.
Medications are only effective when they reach their site of action, therefore the different routes of drug administration and dosage forms are used to reach the target area to act through several types of the dosage form. Medications are administered through various routes of administration that depend on the way of absorption necessary for their therapeutic effect.
Importance of dosage forms:
Appropriate dosage forms are required to protect the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) from the influences of atmospheric conditions such as temperature, humidity, or oxygen, improve therapeutic activity, and patient compliance. It is also required to protect the drug from destruction by gastric acid in the stomach upon oral administration, to mask the unpleasant taste and odor, and for providing extended drug action through controlled release mechanisms.
The need for dosage forms is as follows.
- To provide an accurate dose to the target tissue
- To protect the drug e.g. coated tablets
- To protect gastric juice
- To masking taste and odor
- To bypass the first-pass metabolism
- To provide rapid or sustained or controlled release medication
- To insert medicine into the cavities of the body
Different types of dosage forms:
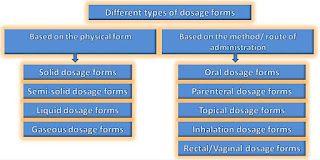
The dosage forms are the different drug product forms by which the medication is administered and they are classified into two types such as according to the route of drug administration and according to the physical form.
Depending on the physical form, the dosage forms are of several types which are as follows.
1. Solid dosage form:
Solid dosage forms are the most commonly used dosage form as compared to other dosage forms and it is one of the most commonly prescribed dosage forms by a doctor as it offers several advantages.
E.g. tablets, capsules (hard/soft gelatin), suppositories, troches, powders, pellets, lozenges, caplets, and granules, etc.
2. Semisolid dosage form:
The semisolid dosage form is neither solid nor liquid, though, it is a mixture or combination of both, and it is used for both local and systemic effects. It can directly apply to the skin, buccal tissue, cornea, rectal tissue, cornea, and outer ear lining nasal mucosa.
E.g. Gels, creams, paste, ointments, suppositories, lotions, and liniment, etc.
3. Liquid dosage form:
The liquid form of medication dose for administration or consumption, and can be administered as oral or parenteral, or topical. It can be classified as monophasic and biphasic and is useful for patients who have difficulty swallowing solid medicines, especially for child and elderly patients.
E.g. Emulsion, suspension, syrup, elixirs, parenteral preparations, linctuses, lotions, eardrops, eardrops, mouthwash, nasal drops, and gargles, etc.
4. Gaseous dosage form:
In gaseous dosage forms, the active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) are given in the form of gas, are packed in a special container which gets released upon applying pressure. It is used in the nose and mouth for local application and topical application on the skin.
E.g. Inhalers, aerosols, vaporizers, sprays, and nebulizers or atomizers.
Depending on the route of administration, the dosage forms are of several types which are as follows.
1. Oral dosage form:
Oral administration is a route of administration where medication is taken through the mouth. It is the most commonly used route for the treatment of the disease as it is the safest, convenient, and economical way to deliver drugs. Most drugs in this route are absorbed by the small intestine however some are absorbed by the stomach and colon.
E.g. Tablets, capsules, liquids, granules, powders, suspension, and syrup, etc.
2. Parenteral dosage form:
Drugs are administered in a parenteral manner, which means that the drug is injected directly into the body using a syringe and needle or intravenous infusion set. The common parenteral routes are intravenous (in a vein), intramuscular (in a muscle), subcutaneous (under the skin), and intra-dermal (under the epidermis) route, they each have needs administer properly by the specific skill.
This route can be chosen when the drug is poorly absorbed from the stomach or metabolized during its passage through the liver or inactivated by digestive enzymes or if the patient is unable to take orally or to achieve a rapid onset of action.
E.g. Injections, solutions, or suspensions
3. Topical dosage form:
The topical dosage form is applied to a particular part of the body such as the skin or mucous membrane to produce the local and systemic effects effect of the drug.
It is preferred over other routes because it provides local therapeutic activity when applied to the skin or mucous membrane and does not cause pain, there is no issue with the unpleasant taste and odor of the drug.
E.g. Ointment, paste, cream, gel, lotion, eye drops (ophthalmic), ear drops (otic), and transdermal patch, etc.
4. Inhalation dosage form:
The inhalation route of administration involves the administration of a drug through the respiratory system with an appropriate combination of excipients in the form of gas, fine powder, and aerosols, usually by oral or nasal inhalation. It is more effective in local and systemic drug delivery for pulmonary and non-pulmonary diseases.
E.g. inhaler, aerosol, nebulizer, and vaporizer, etc.
5. Instilled in the body cavities:
Rectal and vaginal administration dosage forms are used for local as well as systemic drug delivery and may provide some unique advantages.
E.g. suppository pessary and douche etc.
Commonly asked questions on dosage forms are as follows.
On what basis can the pharmaceutical dosage forms be classified?
The dosage forms can be classified based on the physical form of the drug and the route of administration.
What is the most common route of administration?
The oral route is one of the most commonly used routes of administration because it is cost-effective and more convenient for the patient.
What are the types of modified release drug delivery systems?
A variety of modified dosage forms are formulated to reduce side effects as well as increase patient compliance by reducing the frequency of dosing. Sustained-release, delayed-release, extended-release, controlled-release, targeted-release, prolonged-action, and repeat-action dosage forms are the types of modified dosage forms.
No comments:
Post a Comment