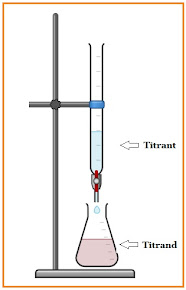
The major difference between titrant and titrand is that the titrant is the reagent of known concentration which is filled in the burette, while titrand is the substance being titrated, generally which is in the conical flask.
Titrimetry, or titration, is a volumetric analysis that determines the concentration of analyte in a sample solution. It consists of a titrant that is filled into a burette, a pipette that is used to introduce the titrand into the conical flask where the reaction occurs. A titrant of known concentration is added until the reaction is complete i.e. chemical equivalence point.
The titration's endpoint is the point at which the reaction is complete. To find the endpoint, an indicator is used which changes the color of the solution at the endpoint or equivalence point. An instrumental method, such as a pH meter, potentiometer, or conductivity, can be used instead. Based on the chemical reaction between the titrant and the solute, there are four types of titrations, namely acid-base titration, redox titration, complexometric titration, and precipitation titration.
|
Table of Contents |
What is titrant?
In analytical chemistry, a titrant is a solution with a known concentration that is added to another solution to find out the concentration of a second chemical species. The titrant is also known as the reagent, titrator, or standard solution.
In simple words, a titrant is a known concentrated solution filled in a burette that is added to a solution whose concentration is to be determined.
What is titrand?
In analytical chemistry, a titrand is a solution whose concentration is determined by titration. It is feasible to determine the analyte concentration by reacting a known concentration and volume of a titrant with the analyte.
Example of titrant and titrand:
For example, the acid-base titration of sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid, in which NaOH is titrant and HCL is titrand.
Difference between titrant and titrand:
The major difference between titrant and titrand is that the titrant is the reagent of known concentration which is filled in the burette, while titrand is the substance being titrated, generally which is in the conical flask.
Is the titrant in the burette?
Yes, the titrant is always in the burette that is added to a solution whose concentration is to be determined.
What is titrant and titrand in titrimetric analysis?
In titrimetry, a reagent known as the titrant is added to a solution containing a reagent known as the titrand, and the two are allowed to react.
What is the difference between the titrant and the analyte?
The basic difference between the titrant and the analyte is that the analyte is any compound that undergoing analysis, whereas titrant is a reagent with a known concentration and volume that is used in titrations.
You may also like this
Good concept
ReplyDelete