Learn the principle of column chromatography which is works on four different mechanisms. Also, learn its types, applications, advantages, and how to do column chromatography.
What is column chromatography?
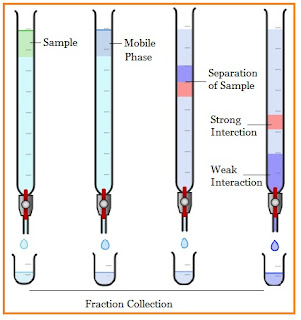
Column chromatography is one of the most effective methods for separating and purifying solid and liquid samples, in which the stationary phase is a solid and a liquid is a mobile phase. In column chromatography, the column is filled with solid support, (silica gel) and a mobile phase, the sample component is placed on top of the column, and then it moves from the solid support under the force of gravity.
The different sample components to be separated migrate at different rates through the column. The components are separated based on their varying affinity for the stationary phase, hence they are separated into fractions.
Column chromatography principle:
The principle involved in column chromatography is that the adsorption of the solutes of a mobile phase through a stationary phase and separates the combination into individual analytes. It is based on the affinity towards the stationary phase and mobile phase. The molecules that have a lower affinity for the stationary phase that they elute rapidly, and molecules that have more affinity for the stationary phase elute slowly.
| Table of contents |
Before starting the column chromatography experiment, we must understand the various steps required to perform the process.
Adsorbent or Stationary Phase:
The alumina and silica gel is two commonly used adsorbents for column chromatography. Both are the solid material that has a good adsorption property, are chemically inert, have high mechanical stability and are suitable for separating different molecules.
Mobile Phase or solvent mixture:
The mobile phase is a solvent or solvent mixture, it acts as an eluting agent and it helps separate the sample molecules.
Types of column packing in column chromatography:
Typically, two methods are used to prepare columns.
Dry method: In this process, the column is filled with dry silica powder. Subsequently, an appropriate solvent or mobile phase is flushed through it until all the silica is wet and settled. The column still needs to keep wet with solvent from this point until the end.
Wet method: In the wet packing, silica and solvent slurry is prepared and then transfer into the column.
Experimental procedure of column chromatography:
- Put the column in a vertical position with the help of an appropriate stand.
- Place a glass wool plug at the bottom of the column.
- There are different ways to prepare columns but most analysts preferred slurry methods. Prepare the silica gel slurry with an appropriate solvent, and then gently pour it into the column.
- Open the tap and drain out the certain solvent. The mobile phase layer should always cover the adsorbent; if not, cracks in the column will form.
- Add the sample mixture to the column in such a way that it does not disturb its upper layer.
- Cautiously open the stop-cock and maintain the solvent level. The solvent needs to be repeatedly added as needed during the entire process.
- The components of the mixture run down the column and separate according to their polarity (forming separate bands).
- Collect the constituents individually when it arrives at the end of the column.
Types of column chromatography:
There are four types of column chromatography available based on the stationary phase, and they operate on various mechanisms.
1. Adsorption chromatography: This is a separation process, in which the mixture components are adsorbed on the adsorbent surface.
2. Ion-exchange chromatography: In which ion exchange resin is the stationary phase.
3. Partition chromatography: For partition chromatography both the stationary phase and the mobile phase is liquid.
4. Gel chromatography: In which the separation is carried out in a column filled with gel.
Column chromatography applications:
- Separating compound mixtures make column chromatography very effective.
- The column chromatography can be used to separate drugs and components of several classes such as aggregates, plant extracts, amino acids, glycosides, and alkaloids.
- Impurities can be isolated in a formula, using the correct mobile phase and stationary phase.
- The pharmaceutical industries usually employ column chromatography to purify compounds.
- It is used for estimating drugs from drug formulations.
- It is possible to separate essential constituents from the crude extract active constituents, plant extracts, and formulations.
- Column chromatography is a flexible method of purification used to separate compounds within a solution.
Advantages of column chromatography:
- Column chromatography can be used to separate all kinds of complex mixtures.
- It is an inexpensive, robust, and versatile method of separation.
- Column chromatography can isolate both small and large quantities of mixtures.
- It has a wide range of mobile phages.
- In preparative type chromatography, the molecules can be separated and reused.
- Automation can be implemented.
Disadvantages of column chromatography:
- It takes longer to separate the compounds by this method.
- You need the expertise to handle the equipment and process.
- It is less accurate and precise than other chromatographic techniques.
- Automation makes things more complex and expensive.
- This requires more solvent to separate the components.
The questions commonly asked about chromatography are as follows.
What is column chromatography?
Column chromatography is a commonly used method of separating the compounds from complex mixtures. Chromatography, when performed in a column, is called column chromatography.
What is the basic principle of Column Chromatography?
The basic principle involved in column chromatography is to adsorb solutes of the solution using a stationary phase and separate the sample mixture further into individual components.
What is the principle of adsorption chromatography?
Adsorption chromatography is based on the principle that some adsorbents (solid material) will hold the molecule on their surface.
What is the major advantage of Column Chromatography?
The main advantage of column chromatography is that any type and amount of mixture can be separated by a wider choice of mobile Phase.
What is the difference between column chromatography and paper chromatography?
The major difference between column chromatography and paper chromatography is that paper chromatography works under gravity and column chromatography works against gravity. another major difference between column and paper chromatography is that the stationary phase used in the separation.
Why TLC used before column chromatography?
Column chromatography works like TLC and uses both similar stationary and mobile phases. Therefore the thin layer chromatography is used to obtain a suitable solvent system and Rf value for column chromatography.
You may also like this
Principle and Procedure of Thin Layer Chromatography
Principle and Procedure of Paper chromatography
Principle and Procedure of HPTLC Chromatography
Different types of Column Chromatography
Definition of Partition column chromatography
Principle and Application of Partition Chromatography
Pharmaceutical Applications of Column Chromatography
Factors Affecting Separation in Column Chromatography
Different types of Column Chromatography
Pharmaceutical Applications of Column Chromatography
Factors Affecting Separation in Column Chromatography
Definition of Partition column chromatography
Advantages and Disadvantages of Column Chromatography
Different types of Column Chromatography
Introduction to Thin Layer Chromatography