Capsules come in two types, hard gelatin capsules, and soft gelatin capsules, depending on the physical state of the drug to be filled. They are of different sizes and shapes and contain a single or more than one active ingredient.
Different types of routes and dosage forms are used to diagnose various diseases. Dosage forms are methods of delivering medication within the body to obtain the best possible benefit with the least possible adverse effects.
The different types of dosage forms are available such as solid, semisolid, gaseous, and liquid dosage forms but the oral-solid dosage form is one of the most used. They provide significant applications and advantages and can be in the form of powders, sachets, granules, tablets, and capsules. They are intended for oral administration.
| Table of Contents: |
What is capsule in pharmacy?
The capsule is a solid dosage form of medication in which one or more active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) and the excipients are enclosed in either a hard or soft soluble gelatin container. It is divided into solid drugs and liquid drugs depending on the physical state of the drug to be filled.Generally, the manufacturing process of capsules involves weighing, preparing ingredients, mixing, filling into capsules, and packing, etc.
Gelatin capsules often referred to as gel caps, are made from gelatin derived from the collagen of animal skin or bone. Cellulose, a significant structural component in plants, is used to make vegetable capsules, which were first introduced in 1989. Gelatin capsules are more widely used than vegetarian capsules in the current market due to the cheaper production cost.
Example: Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is the key constituent in vegetarian capsules.
Definition of a capsule in industrial pharmacy:
According to the United States Pharmacopeia capsule is defined as solid dosage forms in which the active ingredients are encapsulated in a hard or soft container or shell.
Types of capsules with examples:
According to the raw material used in the formulation, the capsule can also be divided into a hard gelatin capsule, soft gelatin capsule, HPMC capsule, pullulan capsule, starch capsule, enteric capsules, metallic capsules, etc.
Two types of gelatin are used to prepare different types of capsules, type-A gelatin, and type-B gelatin.
Type-A gelatin: It is produced from acid hydrolysis and shows an isoelectric point in the region of pH 7.00 and 09.00.
Type-B gelatin: Type-B gelatin is derived from alkali hydrolysis; it exhibits an isoelectric point in the region of pH 4.7 and 5.4.
Hard-shelled capsules:
A hard gelatin capsule (Two-piece gel encapsulation) is a type of capsule which is commonly used to contain medicine in the form of dry powder or granules. It consists of two parts, one is the body and the other is the cap of the capsule (prefabricated, cylindrical sections), each of which has one rounded, closed-end, and one open end.
The hard gelatin capsules dry in nature may be colorless or may be available in different colors as needed. It provides great versatility for multi-particulate administration and the combination of various drugs within the same solid dosage unit. Hard gelatin shell is made of titanium dioxide, plasticizer as well as coloring agents.
Soft-shelled capsules:
Soft gelatin capsule (Single-piece gel encapsulation) is a type of capsule also called soft gel or soft elastic capsules, which are sealed one-piece containing a liquid or a semisolid fill without a bubble of air or gas. In the oil-based solution, the drug or medicine is dissolved and when the capsule is swallowed, it dissolves within the body, releases the drug into the stomach.
The shell of the soft gel capsule is composed of sugars, opacifying agents, plasticizers, water, preservatives gelatin, gelatin, sugars, coloring agents, and a plasticizer such as glycerin and/or sorbitol(s). Soft gel capsules come in a range of shapes and sizes, including cylindrical (0.15–25 ml), pear-shaped (0.3–5 ml), spherical (0.05–5 ml), ovoid (0.05–7 ml), and tubes (0.3–5 ml).
HPMC capsules:
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is a kind of cellulose known as hypromellose which is obtained by the hydrolysis of plants and is made by etherification. HPMC capsules are composed of HPMC and purified water and come in sizes ranging from 00 to 4. HPMC is better for moisture-sensitive products, hygroscopic materials, and low relative-humidity applications than hard gelatin.
Since it is not of animal origin, it has been used as dietary supplements, nutraceuticals, and herbal products in the food and pharmacy industries all over the world, and it is listed in the world's official pharmacopeia.
Pullulan capsule:
Tapioca is naturally fermented into pullulan, which is used to make these vegetarian capsules. Pullulan is a mature food additive that is a water-soluble mucopolysaccharide. Pullulan and purified water are the major ingredients in the pullulan capsule which provide a high oxygen barrier.
Due to its good film-forming properties and other exceptional characteristics, it has become the ideal raw material for capsule production, substituting animal gelatin to produce pure natural vegetarian empty capsules.
Starch capsules:
The starch capsule is a type of capsule made from potato starch and is a very effective alternate delivery mechanism for orally given compounds. They have a pH-independent dissolution and are appropriate for enteric coating. It has a moisture level of 12 to 14 % w/w, with more than 30 percent tightly bound.
These capsules are recognized to have several advantages over traditional capsules, including low static charge, low moisture content, low humidity levels, and others, all of which contribute to the safety of the contents within the capsules.
Fish gelatin capsules:
Fish gelatin capsules are types of capsule which is preferred for filling marine supplements for example rich in fish oil. It is one of the most important types of gelatins derived from non-mammalian sources, and it can thus be used as a substitute for mammalian gelatin in a variety of food and pharmaceutical applications.
Enteric-coated capsules:
Enteric-coated capsules have an acid-resistant coating that keeps them from dissolving as they pass through the stomach. The capsules are only activated when they travel through an alkaline environment, which is normally when they reach the small intestine, with a pH value of 5.5 or higher.
Metallic capsules:
Metallic capsules also referred to as pearl capsules, are made up of pearl pigments as coloring agents. They come in a variety of attractive colors to accommodate customer preferences.
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) capsules:
Capsules made of PVA can be used to fill insoluble drugs dissolved in polyethylene glycol (PEG) 400.
PVA is a synthetic polymer that has long been used as a coating agent for tablets and capsules in the pharmaceutical industry. PVA has limited oxygen permeability, resulting in a high oxygen barrier.
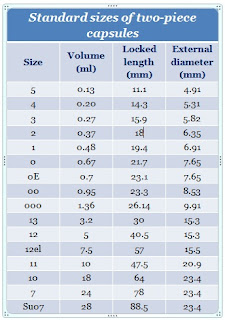
Different sizes of capsules:
Two-piece capsules come in different sizes (5 to su07) volume (0.13 ml to 28 ml), locked length (11.1 to 88.5 mm), and external diameter (4.91 to 23.4) to meet the needs of the customer. The following is a list of the various standard sizes of two-piece capsules.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ):
What are the different types of capsule shells?
The capsule is a type of solid dosage form with hard or soft shells. Hard gelatin capsule, soft gelatin capsule, HPMC capsule, pullulan capsule, and enteric-coated capsule are the types of capsule shell.
What is the difference between hard gelatin capsules and soft gelatin capsules?
The major difference between hard gelatin capsules and soft gelatin capsules is that the hard gelatin capsule is used for those medicines which include dry powder, and granules, while soft gelatin is used for a drug that contains liquid and semi-solid.
What are the types of tablet coating?
Enteric coating, sugar coating, gelatin coating, film coating, and compression coating are some of the types of tablet coating.
What is the advantage of capsules?
The major advantage of the capsule is that we can prepare a unique mixture of drugs or ingredients in a single dose that is not possible in other types of solid dosage forms.
What types of diseases can be diagnosed with capsule endoscopy?
Capsule endoscopy is used to view parts of the GI tract that other types of endoscopy cannot see.
References:
- Wikipedia contributors. Capsule (pharmacy). In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Capsule_(pharmacy)&oldid=1058802361
- EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA (EP) 8.0
- S. Arora, et al., “Capsules” in Theory and Practice of Industrial Pharmacy by Lachmann and Lieberman, R.K. Khar, S. P. Vyas, F.J. Ahmad, and G.K. Jain, Eds. (CBS Publishers & Distributors, 4th ed., 2013), pp. 546-578.
- Dr. Sven Stegemann, Capsugel, Bornem, Hard gelatin capsules today – and tomorrow (2nd edition 2002), Retrieved from https://cpsl-web.s3.amazonaws.com/kc/library/hard-gelatin-capsules-today-and-tomorrow.pdf
You may also like this
No comments:
Post a Comment